Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV) is a respiratory virus that commonly infects people of all ages. Discovered in 2001, it is closely related to respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and can cause a range of illnesses, from mild cold-like symptoms to severe respiratory infections. While hMPV is not as well-known as influenza or COVID-19, it plays a significant role in seasonal respiratory illnesses, especially in children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
In recent years, hMPV has gained more attention due to its increased prevalence during the winter and spring months, raising concerns among healthcare professionals. This article delves into what hMPV is, its symptoms, how it spreads, treatment options, and ways to prevent infection.
What is Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV)?
hMPV belongs to the Paramyxoviridae family, the same family as RSV, mumps, and measles. It primarily affects the upper and lower respiratory tract, causing symptoms that range from mild to severe, depending on the individual’s age and health condition. The virus is more common in children under the age of 5, but adults can also become infected, particularly during outbreaks.
Symptoms of hMPV Infection
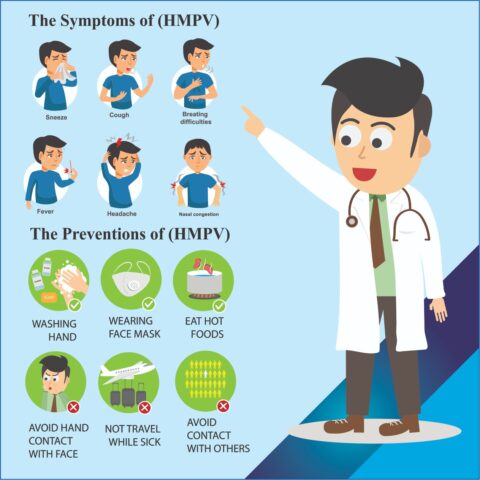
The symptoms of hMPV can vary widely, from mild cold-like signs to more severe respiratory issues. Common symptoms include:
• Runny nose
• Cough
• Fever
• Sore throat
• Shortness of breath
• Wheezing
In severe cases, hMPV can lead to complications such as bronchitis, pneumonia, or bronchiolitis, particularly in high-risk groups like infants, elderly people, and those with underlying health conditions.
How Does hMPV Spread?
Like many respiratory viruses, hMPV spreads through:
• Respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
• Direct contact with contaminated surfaces or objects.
• Close personal contact such as shaking hands or hugging an infected person.
The virus is highly contagious and can survive on surfaces for several hours, making proper hygiene crucial in preventing its spread.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing hMPV typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. Doctors may recommend tests such as:
• PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) tests, which detect the virus’s genetic material.
• Rapid antigen tests that identify viral proteins.
Currently, there is no specific antiviral treatment for hMPV. In most cases, the infection resolves on its own with supportive care. Common treatment options include:
• Rest and hydration to help the body recover.
• Over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms like fever and congestion.
• In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary, particularly for those who develop complications such as pneumonia.
Prevention Tips

Preventing hMPV infection involves many of the same strategies used to prevent other respiratory illnesses. Key prevention tips include:
1. Practice good hand hygiene: Wash hands regularly with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
2. Avoid close contact with individuals showing symptoms of respiratory illness.
3. Disinfect frequently-touched surfaces, such as doorknobs, toys, and electronic devices.
4. Wear a mask during outbreaks to reduce the risk of inhaling respiratory droplets.
5. Boost your immune system through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep.
Although no vaccine is currently available for hMPV, researchers are working on developing one. Until then, following these preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
Why is Awareness About hMPV Important?
Raising awareness about hMPV is essential because its symptoms can be similar to those of other respiratory illnesses, such as RSV, influenza, and COVID-19. Increased awareness can help individuals seek medical attention promptly, reducing the risk of severe complications. Moreover, understanding the virus’s transmission methods can encourage better hygiene practices, ultimately lowering the spread of the infection.
Conclusion
Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV) is a common yet often overlooked respiratory virus that can cause serious illness in vulnerable populations. While most people recover with minimal treatment, it can lead to severe respiratory issues in high-risk groups. By practicing good hygiene, seeking medical advice when necessary, and staying informed, individuals can reduce their risk of infection and contribute to controlling the spread of this virus. As research continues to progress, we may see new advancements in the prevention and treatment of hMPV in the near future.